Online IP Address Converter - CLICK HERE
IP addresses
1. Physical Addresses
2. Port Addresses
3. Logical Addresses
1. What is a physical Address (MAC address)
·
06
bytes long / 48 bits long
·
Cannot
be changed by the user
·
Represented
in hexadecimal format
·
Engaged
with the data link layer in the OSI model
How to find your MAC address in Windows
1. Click on the Windows button on the bottom
left corner of your screen or press the Windows button on your keyboard.
2. Type ipconfig /all and then enter.
3. Under the physical address, you can see your MAC address.
2. What is a port address
·
02
bytes long / 16 bits long
· Engaged with the transport layer in the OSI model
3. What is a Logical address (IP address)
·
Engaged
with the Network layer in the OSI model
·
Unique
for particular hosts connected to the internet
·
User
can configure/change manually
What are the Versions of IP addresses? (Logical Addresses)
1. IPV4
·
IP
Version 04
· 04 bytes long / 32 bits long
2. IPV6
·
IP
Version 06
·
16
bytes long / 128 bits long
How to convert IP addresses from binary notation to the dotted decimal notation?
Let’s take the first byte (08 bits) of an IP address from binary notation.
All bytes of the address from binary notation can be written as this.
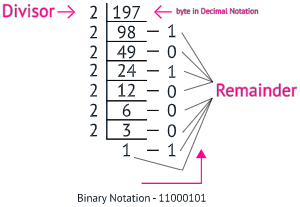
How to convert IP addresses from dotted-decimal notation to binary notation?
Let’s take the first byte of the IP address. We have to divide it from '2' until the end. The answer is from bottom to top.
________________________________________________________________________________
Online IP Address Converter - CLICK HERE
IPv4
addresses can be divided into 05 classes
1
Class
A
2
Class
B
3
Class
C
4
Class
D
5
Class
E
How to find the class in IP address?
1. Binary Notation
The IP address
has a total of 04 bytes. One byte of an IP address has a total of 08 bits. Below are all
considered from the 1st byte of an IP address.
1st
bit = 0 (0
- - - - - - -) Class A
1st
bit = 1 2nd bit =
0 (10
- - - - - -) Class B
1st
bit = 1 2nd bit =
1 3rd bit = 0 (110
- - - - -) Class C
1st
bit = 1 2nd bit =
1 3rd bit = 1 4th bit = 0 (1110 - - - -) Class D
1st
bit = 1 2nd bit =
1 3rd bit = 1 4th bit = 1 (1111 - - - -) Class E
Example:
00000001
00001101 11110100 10001000 – Class A
11000001 00001101 11110100 10001000 – Class C
2. Decimal Notation
If the,
First byte
is from 0 to 127 – Class A
First byte
is from 128 to 191 – Class B
First byte
is from 192 to 223 – Class C
First byte
is from 224 to 239 – Class D
First byte
is from 240 to 255 – Class E
Example
1:
Binary - 11000001 00001101 11110100
10001000 – Class C
After
converting to the decimal notation,
Decimal - 193 . 13 . 244
. 136
193 is
in between 192 & 223. Then the IP address is considered as Class C.
Example
2:
Decimal
- 228.12.14.25
228 is in between 224 & 239. Then the IP address is considered as Class D.
________________________________________________________________________________
What is Net ID and Host ID?
Each IP
address has two parts.
1. Network ID
2. Host ID
Example:
210.25.14.56
Class : C
Network ID : 210.25.14
Host ID : 56
Example:
176.152.34.56
Class : B
Network ID : 176.152
Host ID : 34.56
How to find the network address?
Here we
have to consider the Class A, Class B and Class C addresses only, since they
are used for general purposes IPv4 addresses.
First, you
have to find the class of the given IP address.
If it is a
Class A address, then the Network ID will be the first byte of the IP
address and the Network Address can be written as Network ID. 0.
0. 0
Example:
IP
address : 103.54.25.4
Class : Class A
Network
ID : 103
Network
Address : 103.0.0.0
______________________________________________________________________________
If it is a
Class B address, then the Network ID will be the first 02 bytes of the
IP address and the Network Address can be written as Network ID.
0. 0
Example:
IP
address : 168.44.25.41
Class : Class B
Network
ID : 168.44
Network
Address : 168.44.0.0
_______________________________________________________________________________
If it is a Class
C address, then the Network ID will be the first 03 bytes of the IP
address and the Network Address can be written as Network ID. 0
Example:
IP
address : 195.54.25.4
Class : Class C
Network
ID : 195.54.25
Network
Address : 195.54.25.0
_______________________________________________________________________________
How to find the Broadcast address?
First, you
have to find the class of the given IP address.
If it is a
Class A address, then the Host ID will be the last 03 bytes of the IP
address and the Broadcast Address can be written as Network ID.
255. 255. 255
Example:
IP
address :
50.60.70.5
Class : Class A
Network
ID : 50
Network
Address : 50.0.0.0
Host ID : 60.70.5
Broadcast
Address : 50.255.255.255
In the case of Class
A addresses, 03 bytes are assigned for Host ID. That means,
The last 03
bytes have a total of 24 bits. Then the total number of host addresses = (2^24) –
2 = 16777214
(02
addresses reserved for broadcast and network addresses)
_____________________________________________________________________________
If it is a
Class B address, then the Host ID will be the last 02 bytes of the IP
address and the Broadcast Address can be written as Network ID.
255. 255
Example:
IP
address :
143.32.80.24
Class : Class B
Network
ID : 143.32
Network
Address : 143.32.0.0
Host ID : 80.24
Broadcast
Address : 143.32.255.255
In the case of Class
B addresses, 02 bytes are assigned for Host ID. That means,
The last 02
bytes have a total of 16 bits. Then the total number of host addresses = (2^16) –
2 = 65534
(02
addresses reserved for broadcast and network addresses)
_____________________________________________________________________________
If it is a
Class C address, then the Host ID will be the last byte of the IP
address and the Broadcast Address can be written as Network ID.
255
Example:
IP
address :
200.32.29.201
Class : Class C
Network
ID : 200.32.29
Network
Address : 200.32.29.0
Host ID : 201
Broadcast
Address : 200.32.29.255
In the case of Class
C addresses, 01 byte is assigned for Host ID. That means,
The last 01
byte have a total of 08 bits. Then the total number of host addresses = (2^8) – 2
= 254
(02
addresses reserved for broadcast and network addresses)
_______________________________________________________________________________
Examples
IP
Address : 127.38.155.200
Class : Class A
Subnet
Mask : 255.0.0.0
Network
Address : 127.0.0.0
Broadcast
Address : 127.255.255.255
IP
Address : 192.200.50.107
Class : Class C
Subnet
Mask : 255.255.255.0
Network
Address : 192.200.50.0
Broadcast
Address : 192.200.50.255
IP
Address : 135.45.39.201
Class : Class B
Subnet
Mask : 255.255.0.0
Network
Address : 135.45.0.0
Broadcast
Address : 135.45.255.255
IP
Address : 50.75.70.2
Class : Class A
Subnet
Mask : 255.0.0.0
Network
Address : 50.0.0.0
Broadcast
Address : 50.255.255.255
Online IP Address Converter - CLICK HERE
----------------------------------------------------- The End ---------------------------------------------------------






.jpg)








No comments:
Post a Comment